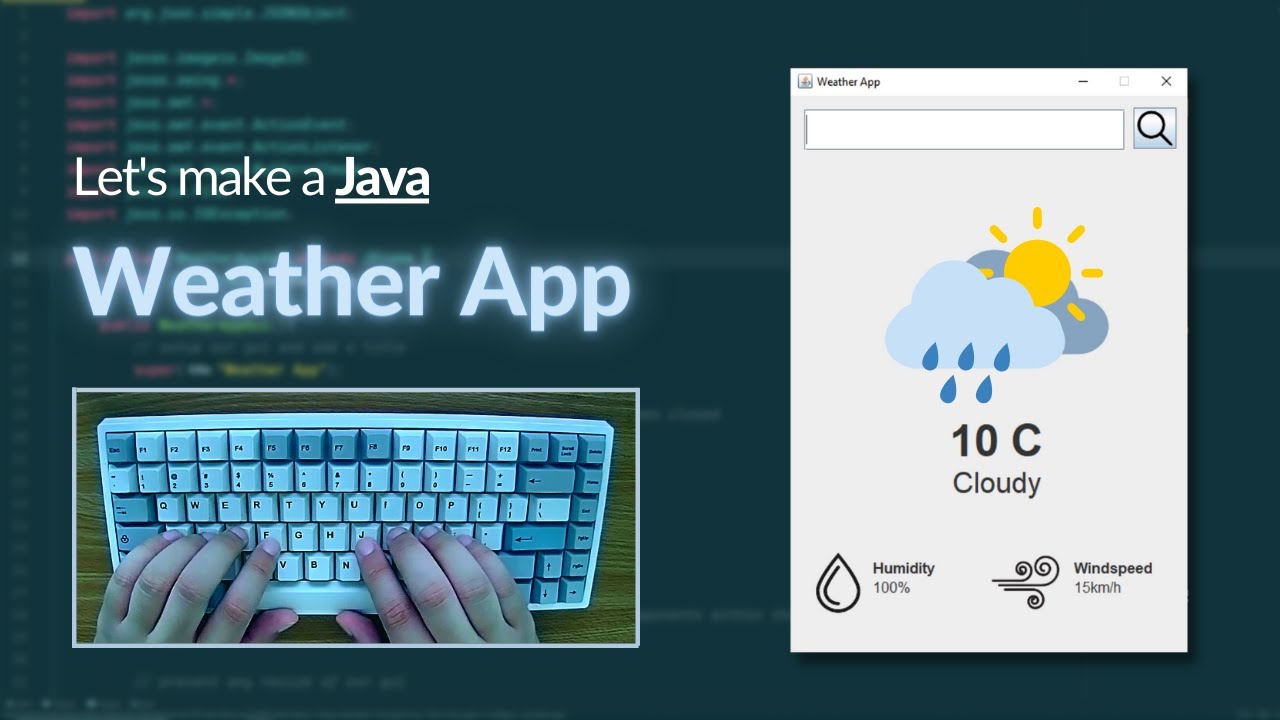
Developing a Weather Forecast App in Java
Weather forecasting applications have become an essential part of daily life, helping users plan travel, outdoor activities, and work schedules. With the growing demand for real-time information, developing a reliable weather forecast app is an excellent project for Java developers. Java remains a popular programming language due to its platform independence, strong ecosystem, and extensive library support. Building a weather forecast app in Java not only enhances practical coding skills but also introduces developers to concepts such as API integration, data parsing, user interface design, and error handling. This project is suitable for both beginners and intermediate developers looking to apply Java in a real-world scenario.
Understanding the Core Features of a Weather App
Before beginning development, it is important to define the core features of the weather application. A basic weather app typically displays current conditions such as temperature, humidity, wind speed, and general weather descriptions. More advanced versions may include hourly and weekly forecasts, weather alerts, and multiple location support. Clearly outlining these features helps in planning the application structure and ensures that development stays focused on user needs, a principle often highlighted in project-based learning environments and decision-making frameworks taught at a Business School in Chennai.
Choosing a Weather API
Weather apps rely on external data sources to provide accurate and up-to-date information. Several public weather APIs are available that offer current conditions and forecast data. When choosing an API, developers should consider factors such as data accuracy, request limits, response format, and documentation quality. Most APIs return data in JSON format, which Java can easily parse using libraries. Registering for an API key and understanding the API endpoints is a crucial step before coding begins.
Setting Up the Java Development Environment
To develop a weather forecast app in Java, a proper development environment must be set up. This includes installing the Java Development Kit (JDK) and selecting an integrated development environment such as IntelliJ IDEA, Eclipse, or NetBeans. A build tool like Maven or Gradle helps manage dependencies and project structure. Organizing the project into clear packages for services, models, and user interface components improves readability and maintainability.
Fetching Weather Data Using HTTP Requests
Once the environment is ready, the next step is fetching weather data from the chosen API. Java provides several ways to make HTTP requests, including built-in libraries and third-party frameworks. The application sends a request to the API endpoint with parameters such as location and API key, then receives a response containing weather data. Handling network errors and timeouts is important to ensure a smooth user experience, especially when connectivity is unstable.
Parsing and Processing API Responses
After receiving the API response, the application must parse the data and extract relevant information. Since most weather APIs return JSON responses, Java developers commonly use JSON parsing libraries to convert the data into usable objects. Creating data models for weather information helps structure the data logically and makes the application easier to maintain and scale. Once parsed, the app can process the data to format values, convert units, and prepare information for display practical skills that are often strengthened through hands-on projects covered in Java Training in Chennai.
Designing the User Interface
The user interface plays a significant role in the usability of a weather app. Depending on the target platform, developers can choose different UI frameworks. For desktop applications, JavaFX or Swing can be used to design interactive interfaces. A clean layout, readable fonts, and intuitive navigation improve user engagement. Displaying weather icons, charts, and color indicators enhances the visual appeal and helps users understand weather conditions at a glance.
Implementing Location-Based Features
A useful weather app allows users to check forecasts for different locations. This can be achieved by enabling manual city input or integrating location services for automatic detection. Managing multiple locations and saving user preferences adds convenience. Implementing location-based features requires careful handling of user input and validation to ensure accurate data retrieval from the API.
Handling Errors and Improving Performance
Error handling is essential for building a reliable application. The app should gracefully manage scenarios such as invalid location inputs, API request failures, or exceeded request limits without disrupting the user experience. Displaying clear and meaningful error messages improves usability and builds user trust. Performance optimization techniques, including caching recently fetched weather data, help minimize unnecessary API calls and enhance response time. Efficient data handling ensures that the application remains responsive as new features are added, an approach commonly emphasized in Programming Courses in Chennai, where developers learn to build scalable and robust applications.
Testing and Deployment
Testing ensures that the weather forecast app works as expected under different scenarios. Unit testing can be used to validate individual components, while integration testing checks API interactions and data flow. Testing the app with various locations and network conditions helps identify potential issues. Once testing is complete, the app can be packaged and deployed. Depending on the platform, this may involve creating executable files or distributing the app through appropriate channels.
Developing a weather forecast app in Java is a practical and rewarding project that combines core programming concepts with real-world application development. It helps developers gain experience in API integration, data processing, UI design, and error handling. By carefully planning features, choosing the right tools, and following best practices, developers can create a reliable and user-friendly weather application. This project not only strengthens Java skills but also builds confidence in developing scalable applications that interact with external data sources.
